Green Logistics: Optimising Sustainability and Business Profitability

The demand on companies to act sustainably has reached an unprecedented level. It is no longer an option, but a key necessity to ensure their long-term viability and success.
In this context, a key concept is emerging that is transforming supply chains: green logistics. Far from being a fad, it has established itself as a key strategy for efficiency, profitability and brand reputation.
What is green logistics?
Green logistics, also known as sustainable logistics, is a comprehensive approach that minimises the environmental impact of all supply chain activities.
It includes everything from raw material sourcing and production to transportation, warehousing, product distribution, and, crucially, reverse logistics.
Its main objective is to balance economic efficiency and commitment to environmental and social sustainability.
The fundamental principles guiding this discipline are clear and forceful:
- Pollution reduction: Reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water and air pollution, and noise generation.
- Optimisation of resource use: Efficient management of energy, water and raw materials.
- Waste minimisation: Encourage reduction, reuse and recycling throughout the chain.
- Maximising efficiency: Achieving more with less, improving processes and reducing unnecessary consumption.
Pillars of green logistics: how it is implemented in practice
Adopting green logistics involves a paradigm shift in multiple operational areas. It is not about implementing one-off measures, but about implementing a coordinated strategy that completely transforms supply chain management:
Intelligent transport and routes:
- Route and load optimisation: The use of advanced software enables the design of more efficient routes, minimising kilometres and fuel consumption, and ensuring that vehicles travel at full capacity.
- Greener fleets: Investing in electric, hybrid or alternative fuel vehicles drastically reduces polluting emissions.
- Intermodal transport: Combining different modes of transport (road, rail, maritime) maximises efficiency and reduces the carbon footprint, especially over long distances.

Sustainable storage and inventory management:
- Energy efficient warehouses: Design or retrofit facilities with LED lighting, smart HVAC systems or even solar panels to reduce energy consumption.
- Just-in-time inventory management: Minimising warehouse stock reduces the need for space, energy for maintenance and the risk of obsolescence or wastage.
Conscientious packaging and containers:
- Sustainable materials: Prioritise the use of recyclable, biodegradable, compostable or reusable materials.
- Efficient design: Reduce the amount of packaging material needed and design packaging that optimises space in transport, avoiding unnecessary “air” on pallets.
Reverse logistics and circular economy:
- Take-back and recycling programmes: Implement efficient systems for the recovery of post-consumer products or materials.
- Reuse and recovery: Transforming waste into new resources, contributing to a more circular economy and reducing dependence on virgin raw materials.
Supply chain collaboration:
- Work closely with suppliers and partners who share the same sustainability values. A truly green supply chain requires the commitment of all links in the supply chain.
Tangible benefits of green logistics for companies
Implementing sustainable logistics practices is not only a matter of ethical responsibility, but also a strategic decision that brings real benefits in several areas:
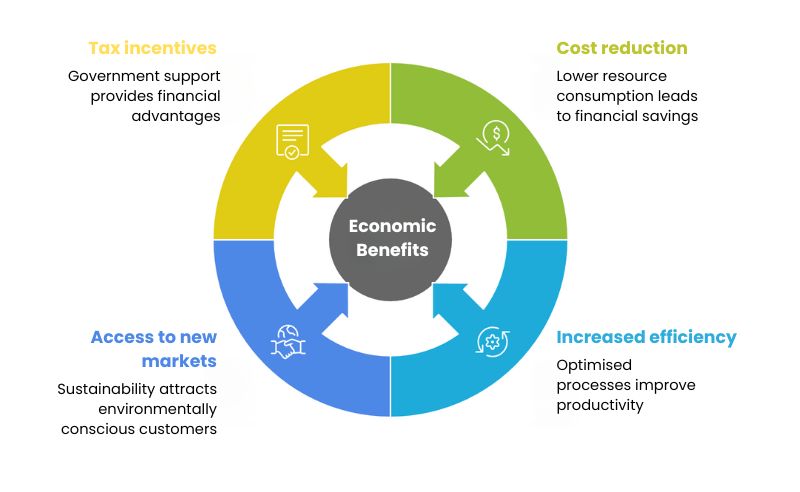
Economic benefits:
- Reduced operating costs: Lower consumption of fuel, energy and packaging materials translates directly into substantial savings on the bottom line.
- Increased operational efficiency: Optimisation of routes, processes, and inventory management leads to a leaner and more productive supply chain.
- Access to new markets and customers: Growing demand for sustainable products and services opens doors to market segments that value environmental responsibility.
- Tax incentives and subsidies: In many regions, companies that invest in sustainability are eligible for government grants and tax benefits.
Environmental benefits:
- Reducing the carbon footprint: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions contributes directly to the fight against climate change.
- Reduced consumption of natural resources: More efficient use of water, energy and raw materials protects ecosystems and ensures the availability of resources for the future.
- Reduced waste and pollution: Less landfill waste and less release of pollutants into the environment.
Image and reputational benefits:
- Strengthening Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): A strong image as a company committed to the environment attracts consumers, investors and talent.
- Competitive advantage and differentiation: In a saturated market, sustainability can be a key factor that distinguishes a company from its competition.
- Attracting and retaining talent: Today’s professionals are looking for companies with strong values and a purpose beyond profit.
An investment in the future
Green logistics is more than just a fad; it is a vital strategy for companies aiming for long-term sustainability and competitiveness in a globalised market.
Implementation challenges, such as initial investment or resistance to change, can be overcome with strategic planning, the use of advanced technology and a strong willingness to innovate.
Adopting green logistics practices is not only a statement of commitment to the planet, but a smart investment that translates into cost savings, increased efficiency and an unbeatable business reputation.
It is time for Spanish and global companies to recognise the immense potential of this transformation and integrate it as a fundamental pillar of their operational and business strategy.
Is your company ready to embark on the path to a greener and more profitable supply chain?
You may also be interested in: