Ecological Drums vs. Conventional Drums

The choice between ecological drums and conventional drums has become a crucial issue in industrial and commercial management, reflecting a significant shift towards sustainability and environmental efficiency.
Below, we explore in depth the differences between these two types of containers, assessing everything from the materials used in their manufacture to their specific applications and the environmental impact they generate.
Materials used in its manufacture
Conventional drums
Conventional drums are primarily made from materials such as petroleum-derived plastic and various metals, including steel and aluminium. While these materials offer great strength and durability, their production and disposal present significant environmental challenges.
Oil extraction and refining, as well as metal mining, are resource- and energy-intensive processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. In addition, recycling these materials can be complex due to the cross-contamination and chemical finishes used.
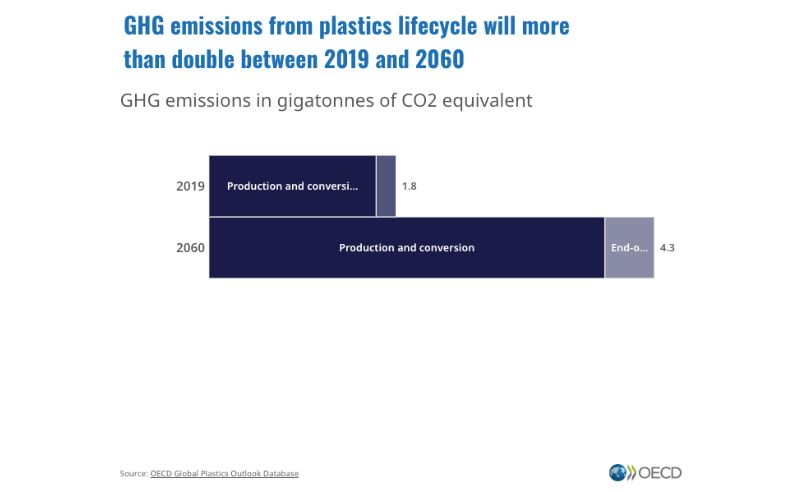
According to the International Energy Agency, plastic production was responsible for about 4% of global energy emissions in 2019.
Ecological drums
In contrast, eco-friendly drums are made from recycled materials, bioplastics or kraft paper. Bioplastics, for example, are derived from renewable sources such as corn and sugar cane, which absorb CO2 as they grow, helping to reduce the carbon footprint.
In addition, these materials are often fully recyclable and biodegradable, making them easy to reintegrate into the product life cycle, reducing waste generation and the use of natural resources.
For example, the use of recycled PET can reduce the carbon footprint associated with the production of new plastics by up to 60%, according to studies published by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
Environmental impact
Conventional drums
The environmental impact of these drums is considerable, mainly due to the non-renewable nature of their materials and the emissions associated with their production.
In addition, once they reach the end of their useful life, their disposal becomes a problem, as many are non-biodegradable and remain in landfills for decades.
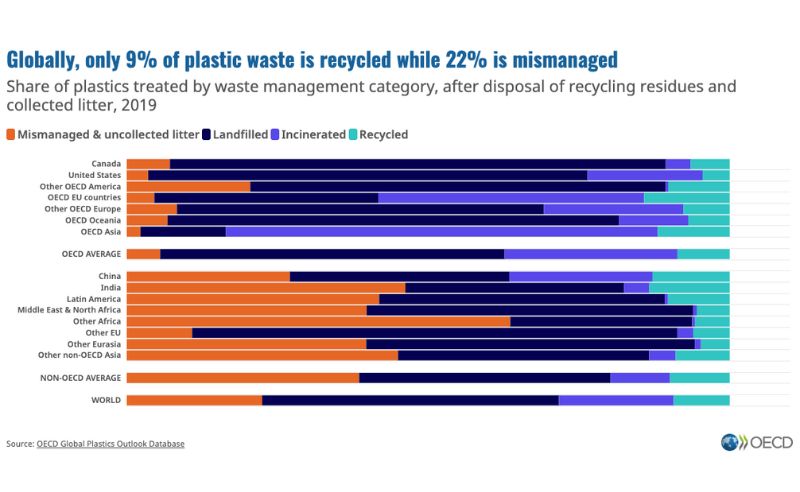
An OECD study highlights that only a small percentage of plastics used in packaging is actually recycled, with the rest contributing to pollution in landfills and oceans.
Ecological drums
These drums are designed to minimise environmental impact. Their manufacture from recycled or biodegradable materials reduces dependence on fossil resources and reduces the carbon emissions associated with production.
In addition, their ability to be recycled or composted at the end of their useful life contributes to a more circular and sustainable economy.
A notable example is the drum recycling programme implemented by companies such as Ecoembes in Spain, which has managed to recycle approximately 78.8% of packaging by 2020.
Cost and accessibility
Conventional drums
These drums are often cheaper at the point of purchase due to economies of scale and established manufacturing processes. However, hidden costs, such as the environmental impact and future expenses associated with their disposal, can make them more expensive in the long run.
Ecological drums
Although the initial cost may be higher, it can be amortised over time through benefits such as tax incentives for sustainable practices, reduced disposal costs and a greener brand image, which can attract environmentally conscious consumers.
The European Commission reports that companies that adopt sustainable practices often experience improved resource efficiency and a reduction of up to 30% in their energy costs.
Applications and usage preferences
Conventional drums
Conventional drums are widely used in industries that require high corrosion resistance and durability, such as the chemical, petroleum and heavy manufacturing industries.
Ecological drums
Green drums are gaining popularity in sectors such as food, pharmaceuticals and consumer goods, where sustainability is a crucial factor.
These sectors benefit from the positive image that green packaging provides, complying with strict environmental regulations and responding to the demands of consumers who prefer sustainable products.
For example, Nestlé has started using bioplastics in its packaging to reduce its reliance on conventional plastics, aligning with its goal of reducing net greenhouse gas emissions to zero by 2050.

The decision to opt for green or conventional drums should be based on a detailed assessment of each company’s specific needs and sustainability goals.
The global trend towards greener practices suggests an increase in the adoption of ecological drums, as companies seek to align themselves with environmentally responsible expectations and improve their public image in an increasingly environmentally conscious marketplace.
Sources:
FAQs
Are eco-drums as robust as conventional drums?
Yes, eco-drums can be designed to offer comparable strength to conventional drums, although their specific suitability may vary depending on the material and design.
Can eco-drums be used for the same range of products as conventional drums?
Yes, eco-drums can be adapted to a wide range of products, although it is always essential to check the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility with different contents.
How are environmentally friendly drums recycled?
Ecological drums are recycled according to the material they are made of. Kraft paper and bioplastics drums are often easier to recycle compared to conventional plastics, and in many cases can be composted.
You may also be interested in: